
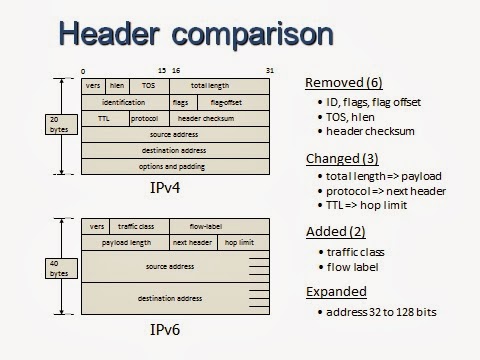
The syntax for identifying the zone is address%zone_ID. If you launch the ipconfig command, you can see the local-link and site-local addresses with their zone IDs. You can display the interface indexes on a host with the command "netsh interface ipv6 show address level=verbose". If a host is only connected to one site, this ID is always 1.
To distinguish this ambiguous link-local address, host A uses the interface index of NIC 1 as the zone ID for the local IP address.įor site-local addresses, the operating system uses the site ID (also called the scope ID). For instance, if host A has two NICs that are connected to two different links (subnets), the same local-link address could have been used for NIC 1 on host A and on host B that is on the link of host A's NIC 2. The purpose of zone IDs is to distinguish these addresses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
